End-to-End Test Management: From Strategy to Success in 2025
End-to-end test management has become crucial for ensuring software quality in today’s complex development environments. Did you know that end-to-end testing has been widely adopted because it helps teams expand their test coverage by adding more detailed test cases than other testing methods like unit and integration testing? This comprehensive approach to quality assurance is particularly valuable as we move toward 2025’s increasingly interconnected systems.
What is end-to-end testing exactly? It’s a software testing method that involves testing an application’s workflow from beginning to end, validating the complete application workflow and simulating real user journeys to ensure all integrated components function seamlessly . Furthermore, end-to-end testing verifies the application from start to end by putting all its components together . In our experience, effective E2E testing accompanies other types of tests like unit and integration tests , creating a robust testing strategy that appeals to a cross-team group including developers, testers, managers, and users .
As we look ahead to 2025, we believe that mastering end-to-end test management will be essential for organizations aiming to deliver high-quality software efficiently. Additionally, E2E testing works particularly well in DevOps environments, where automated testing is integrated into the developer’s day-to-day workflow . However, it’s important to be strategic—experts recommend limiting end-to-end tests to 5-10% of your total test suite, focusing exclusively on critical user journeys and core business logic .
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about end-to-end test management for 2025, from fundamental strategies to advanced implementation techniques that will help you achieve testing success.
What is End-to-End Test Management in 2025?
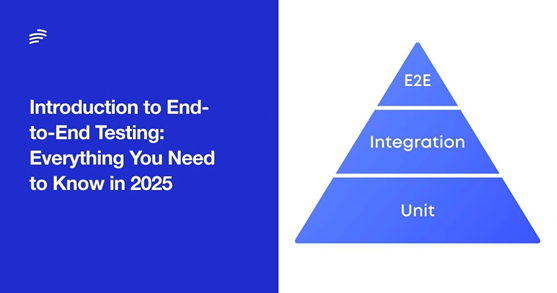
Image Source: Bunnyshell
In 2025, end-to-end test management represents a comprehensive approach to software testing that goes beyond isolated component verification. Understanding its role requires examining what makes it distinct and increasingly vital in today’s complex development environments.
Definition of end-to-end testing vs other testing types
End-to-end (E2E) testing is a methodology that evaluates an application’s workflow from beginning to end, replicating real user scenarios to validate system integration and data integrity. Unlike other testing types, E2E examines how all components function together across the entire technology stack.
When comparing E2E testing with other approaches, several distinctions become clear:
| Testing Type | Primary Focus | Scope | Execution Time | Position in Test Strategy |
| Unit Testing | Individual components | Narrow | Fast | Foundation |
| Integration Testing | Component interactions | Moderate | Medium | Middle layer |
| E2E Testing | Complete user workflows | Broad | Slow | Top layer |
While unit tests verify that individual components work correctly in isolation, integration tests check that these components work well together. In contrast, E2E tests assess the entire application from a user’s perspective, ensuring critical workflows function flawlessly across all subsystems.
Essentially, E2E testing validates not just that individual pieces work, but that they deliver the expected business outcomes when combined. This makes it especially valuable for complex systems with multiple interconnected parts.
How E2E testing fits into the software testing pyramid
The software testing pyramid visually represents how testing should be structured in modern development. According to this model, the most frequently run, cost-efficient tests form the pyramid’s broad base, while more complex, resource-intensive tests occupy the narrower top.
. This strategic positioning indicates that while essential, they should be fewer in number compared to unit and integration tests. This arrangement exists for practical reasons – E2E tests are more time-consuming and resource-intensive than lower-level tests.E2E tests sit at the pyramid’s apex
The pyramid model effectively balances testing needs:
- Bottom layer: Numerous fast unit tests catch component-level issues
- Middle layer: Integration tests verify component interactions
- Top layer: Selective E2E tests validate complete user journeys
Consequently, effective test strategies rely on lower-level tests to catch most bugs early, while using E2E tests to verify that all parts work together correctly in production-like scenarios. Many engineering leaders emphasize that minimal but well-chosen E2E tests focused on core business flows are crucial for preventing catastrophic failures.
Why E2E test management matters more in 2025
E2E test management has gained significance in 2025 due to several converging factors. First, , significantly increasing complexity. When systems consist of numerous independently developed services, E2E testing becomes the only reliable way to ensure they function cohesively.modern software architectures have evolved from monoliths to distributed microservices
Moreover, E2E testing now typically spans multiple applications as business processes operate across different systems. This broader definition reflects the interconnected nature of today’s software landscape, where user journeys frequently cross application boundaries.
E2E test management also matters more in 2025 due to escalating user expectations. When users encounter broken workflows, they rarely blame individual components – they simply experience a failing application. Through simulating real user interactions, E2E tests identify issues that might disrupt a user’s journey before they reach production.
Finally, the rise of automated E2E testing has transformed its practicality. Traditionally limited by execution time and maintenance challenges, modern tools now enable teams to run comprehensive E2E tests efficiently as part of continuous integration pipelines. This automation means companies can be notified immediately if critical user journeys break, allowing teams to fix issues before users experience them.
Key Phases of the End-to-End Testing Process
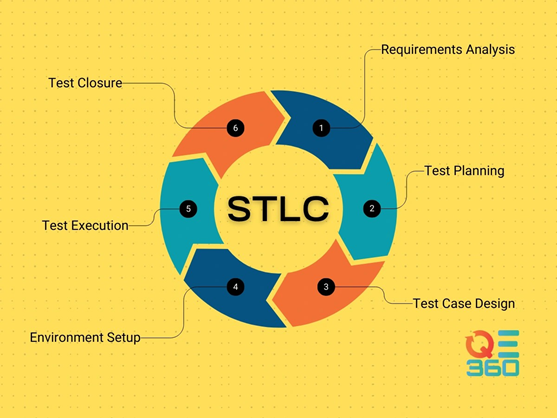
Image Source: QE 360
Implementing successful end-to-end test management requires following a structured process with distinct phases. Each phase builds upon the previous one, ensuring comprehensive test coverage throughout the software development lifecycle.
Test planning and requirement analysis
The foundation of effective end-to-end testing begins with thorough requirement analysis and test planning. Initially, QA teams collaborate with stakeholders to understand the application’s architecture, identify critical user flows, and define functionalities. This phase involves analyzing client requirements, outlining test objectives, determining test scope, and establishing timelines.
Throughout this stage, testers must consider how real users will operate the application and document various test scenarios that reflect realistic user journeys. Early involvement of QA teams in the development process is crucial as it ensures they understand business processes from the beginning. Following this understanding, teams can identify the most business-critical workflows—such as login, checkout, or key integrations—that warrant end-to-end testing.
Test environment setup and data preparation
Prior to execution, creating a properly isolated test environment that mirrors production is essential. This environment must include all necessary components: databases, servers, APIs, and other dependencies. Generally, the test environment should contain similar service configurations, database schemas, and API keys used in production.
For data preparation, teams must decide whether to use repurposed production data (with sensitive information removed) or synthetically generated data that mimics real-world characteristics. Indeed, have become invaluable tools for creating isolated environments with predictable test data, making tests more stable by ensuring consistent starting points for each execution Docker containers.
Test case design and execution
Test case design involves creating detailed scenarios based on user behaviors and system interactions. Test cases should outline different use scenarios pertaining to all components—front end, back end, databases, and APIs. Teams typically choose between two approaches: (covering the entire application across multiple subsystems) and vertical E2E testing (testing individual layers separately).horizontal E2E testing
During execution, testers run these carefully designed tests while monitoring the application’s behavior and data integrity. Execution timing is strategic—teams must decide whether to run tests before deployment (to catch issues early) or after deployment (to verify production functionality), as well as determine appropriate scheduling intervals.
Result analysis and defect tracking
The final phase focuses on evaluating test results against expected outcomes. Testers compare metrics and identify patterns in failures, subsequently performing root-cause analysis on any issues discovered.
Defect tracking involves documenting findings in structured reports that include:
- Title and unique identifier
- Environment details (browser, device, OS)
- Severity and priority classification
- Clear description and reproduction steps
- Supporting evidence (screenshots, logs)
Each defect should be assigned an appropriate status marker to track its progress through resolution. For effective tracking, teams should monitor metrics such as defect details (percentage of identified, closed, or open defects) and test environment availability (scheduled vs. actual testing time).
Top Tools and Frameworks for End-to-End Test Automation
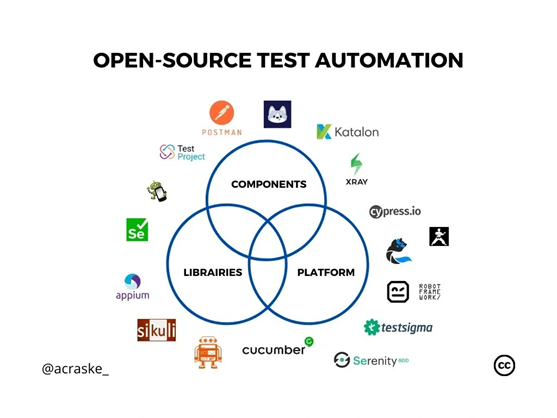
Image Source: Empathy First Media
Selecting the right tools forms the cornerstone of effective end-to-end test automation. As development cycles accelerate, the appropriate framework selection becomes increasingly critical for maintaining quality without sacrificing speed.
Selenium vs Cypress: Use cases and limitations
Selenium, the long-standing open-source leader, offers unmatched for Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge alongside language flexibility (Java, Python, C#, JavaScript). This makes it ideal for polyglot teams needing maximum coverage across diverse environments. Nevertheless, Selenium struggles with synchronization issues that can lead to flaky tests and requires complex setup procedures.cross-browser support
Conversely, Cypress excels in modern web applications with its developer-friendly experience. Its architecture runs directly within the browser, providing , automatic waiting mechanisms, and built-in network traffic control. Though powerful, Cypress has notable limitations: JavaScript-only support, single-tab testing constraints, and less mature cross-browser capabilities. real-time debugging
Playwright and Puppeteer for modern web apps
Microsoft’s Playwright has rapidly gained traction for its powerful cross-browser automation capabilities. It supports Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit with a unified API, making it excellent for ensuring consistent behavior across browsers. With features like auto-waiting, trace viewing, and network interception, Playwright eliminates many sources of test flakiness.
Puppeteer, developed by Google, focuses specifically on Chrome/Chromium automation. While more limited in browser support than Playwright, it excels in Chrome-specific scenarios like performance testing and generating screenshots or PDFs.
Katalon Studio and TestRigor for low-code automation
Katalon Studio bridges the gap between technical and non-technical team members through its dual-scripting interface. Teams can create tests using either a low-code approach or traditional scripting in Groovy/Java. Its Eclipse-based IDE supports web, API, mobile, and desktop testing in a single environment.
TestRigor represents the newest generation of low-code tools, using AI to enable testing through simple plain-language commands. This makes it particularly accessible for manual QA testers with limited programming knowledge.
CI/CD integration with BrowserStack and Jenkins
For true end-to-end test management, integrating testing into CI/CD pipelines is essential. BrowserStack’s Jenkins plugin simplifies this process by enabling test execution across real devices and browsers in the cloud. This integration offers several benefits:
- Automated cross-browser testing as part of build processes
- Embedded test results including videos, logs, and screenshots within Jenkins
- Support for testing internal environments through BrowserStack Local functionality
Playwright similarly integrates smoothly with Jenkins pipelines, allowing teams to archive HTML test reports and publish them to the Jenkins UI for easy access and analysis.
Challenges in Managing E2E Tests at Scale
Image Source: DeviQA
Scaling end-to-end tests introduces unique challenges that can undermine their effectiveness. Despite their value, expanding E2E test suites often reveals limitations that weren’t apparent at smaller scales.
Flaky tests and debugging complexity
Flaky tests—those that inconsistently pass or fail without code changes—represent a significant hurdle in end-to-end testing. These unpredictable failures occur in at many organizations and can quickly erode confidence in the entire test suite. The primary culprits include race conditions, external resource dependencies, and test isolation issues. When flaky tests trigger false failures, teams waste valuable time investigating phantom issues, sometimes requiring entire builds to be retriggered, doubling wait times.4-6% of test runs
Test environment availability and stability
Under these circumstances, maintaining consistent test environments becomes increasingly difficult. Complex applications often consist of multiple microservices, databases, and APIs, each requiring specific configurations. Without proper isolation, test environments frequently suffer from data pollution where leftover data from one test affects others. Containerization through tools like Docker offers a solution by creating isolated environments with predictable test data.
Cross-browser and cross-platform inconsistencies
First and foremost, cross-browser compatibility presents formidable obstacles. Testing across just five major browsers with multiple versions and three operating systems creates , making comprehensive coverage nearly impossible. Each browser employs different rendering engines and JavaScript interpreters that interpret code differently, resulting in subtle but significant variations in behavior.18+ test combinations
Maintaining test scripts in fast-changing UIs
In fact, modern UI frameworks further complicate maintenance efforts. Many popular frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue dynamically generate random element IDs and class names with each render or release cycle. Consequently, tests relying on single identifiers often break when UIs change, increasing maintenance workload and diminishing confidence in test results.
Best Practices for Scalable E2E Test Management
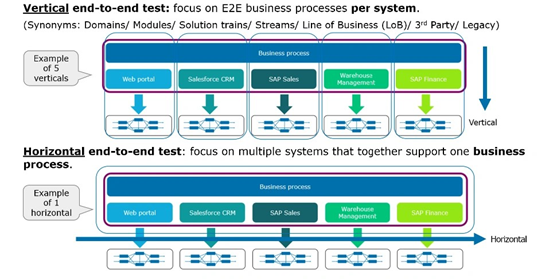
Image Source: Integrated Research
Creating a strategic approach to end-to-end test management remains vital for success in today’s testing landscape. Above all, focus on implementing practices that scale effectively while maintaining quality.
Start with critical user journeys
First thing to remember, prioritize testing the application’s most crucial elements. Identify frequently used features, complex connections, and workflows that directly impact business operations. Quality risk analysis helps determine the most critical E2E processes, focusing on flows that build confidence in your application. Begin by defining desired outcomes, then work backward to create focused test cases rather than attempting comprehensive coverage.
Use vertical and horizontal E2E testing together
Horizontal E2E testing explores application behavior from the user’s perspective across entire systems, whereas vertical testing focuses on specific components. Although horizontal testing should have fewer tests compared to vertical, both approaches complement each other. Together, they ensure comprehensive coverage while validating both technical components and user requirements.
Automate stable flows, test edge cases manually
Balancing automation with manual testing optimizes resources. Automate repetitive tasks and stable workflows, reserving manual testing for complex edge cases and exploratory scenarios. This balanced approach allows QA teams to:
- Focus automation on high-impact, low-complexity test cases
- Leverage manual testing for nuanced user interactions
- Apply the 80/20 rule—achieve 80% of results with 20% of effort
Track metrics: test coverage, execution time flakiness rate
Continuously monitor key performance indicators to measure effectiveness. Track test coverage to assess overall application validation, flakiness rate to identify unreliable tests, and execution time to optimize resource allocation. Additionally, measure defect detection rate and mean time to resolve issues to demonstrate business value.
Conclusion
The comprehensive approach to end-to-end test management stands as a critical factor for software quality assurance heading into 2025. Throughout this article, we’ve explored how E2E testing provides invaluable validation of complete user workflows across interconnected systems, significantly expanding test coverage beyond what unit and integration testing can achieve alone.
Effective E2E test management requires balance. Rather than attempting to test everything, successful teams focus primarily on critical user journeys that directly impact business outcomes. This strategic approach acknowledges that E2E tests should occupy the top of the testing pyramid, complementing rather than replacing lower-level tests.
Additionally, the tools landscape has evolved dramatically, offering solutions for various testing needs. Selenium continues to provide unmatched cross-browser support, while newer frameworks like Cypress and Playwright offer developer-friendly features for modern web applications. Furthermore, low-code options such as Katalon Studio and TestRigor have democratized test automation, making it accessible to team members with limited programming experience.
Nevertheless, scaling E2E testing presents substantial challenges. Flaky tests can undermine confidence in entire test suites, environment stability becomes increasingly difficult to maintain, and cross-browser inconsistencies multiply testing combinations exponentially. Therefore, adopting best practices becomes essential – automating stable flows while manually testing edge cases, combining vertical and horizontal testing approaches, and continuously tracking metrics to measure effectiveness.
As we look toward 2025, organizations that master end-to-end test management will gain a competitive advantage through faster release cycles and higher quality software. The future belongs to teams that can strategically implement E2E testing within their broader quality assurance strategy, creating the right balance between comprehensive coverage and practical execution.
Key Takeaways
Master these essential strategies to build effective end-to-end test management that scales with your development needs in 2025.
• Focus on critical user journeys only – Limit E2E tests to 5-10% of your test suite, targeting business-critical workflows that directly impact user experience and revenue.
• Balance automation with manual testing – Automate stable, repetitive flows while reserving manual testing for complex edge cases and exploratory scenarios using the 80/20 rule.
• Combine vertical and horizontal testing approaches – Use horizontal E2E testing for complete user workflows across systems and vertical testing for specific component validation.
• Track key metrics consistently – Monitor test coverage, flakiness rate, execution time, and defect detection rate to optimize your testing strategy and demonstrate business value.
• Choose tools based on team needs – Select from Selenium for cross-browser coverage, Cypress for developer experience, or Playwright for modern web apps, considering your team’s technical expertise.
Successful E2E test management in 2025 requires strategic thinking rather than comprehensive coverage. Teams that master this balance will deliver higher quality software faster while maintaining confidence in their release cycles.
FAQs
Q1. What is end-to-end testing and why is it important in 2025? End-to-end testing evaluates an application’s complete workflow from start to finish, simulating real user scenarios. It’s crucial in 2025 due to the increasing complexity of software systems, interconnected applications, and high user expectations for seamless experiences.
Q2. How does end-to-end testing differ from other testing types? Unlike unit or integration testing that focus on individual components or their interactions, end-to-end testing examines the entire application stack. It verifies that all parts work together correctly to deliver the expected business outcomes across multiple subsystems.
Q3. What are some popular tools for end-to-end test automation? Popular tools include Selenium for cross-browser support, Cypress for modern web apps, Playwright for powerful cross-browser capabilities, and low-code options like Katalon Studio and TestRigor for teams with limited programming experience.
Q4. What are the main challenges in managing end-to-end tests at scale? Key challenges include dealing with flaky tests, maintaining stable test environments, addressing cross-browser and cross-platform inconsistencies, and keeping test scripts up-to-date with rapidly changing user interfaces.
Q5. What are some best practices for effective end-to-end test management? Best practices include focusing on critical user journeys, combining vertical and horizontal testing approaches, automating stable flows while manually testing edge cases, and consistently tracking metrics like test coverage, flakiness rate, and execution time.
Recent Post
- Artificial Intelligence Compliance Monitoring in Life Sciences: A New Standard for GxP Excellence
- Mastering Computer System Validation: A Practical Guide for Life Sciences
- What is the Importance of the Validation of the System: A Pillar of Life Sciences
- The V-Model in Computer System Validation (CSV): A Strategic Framework for Life Sciences Compliance
- GCP Audit (Good Clinical Practice Audit): Ensuring Clinical Trial Compliance and Quality
